DataView is a software program to visualize and work with structured numeric data. Its aim is to turn data into meaning.
Import data from various sources, such as CSV files, professional EEG equipment, physiological measurements or data from other acquisition systems.
The combination of measured values and observation data creates the context in which you can understand the true meaning of both data sources.
Only DataView allows to time-sync observational data with measurements and thus helps unveiling the raw data meaning.

Watch this video and learn how feeds from different video cameras, eye tracking information and EEG measurements can easily be integrated and analyzed
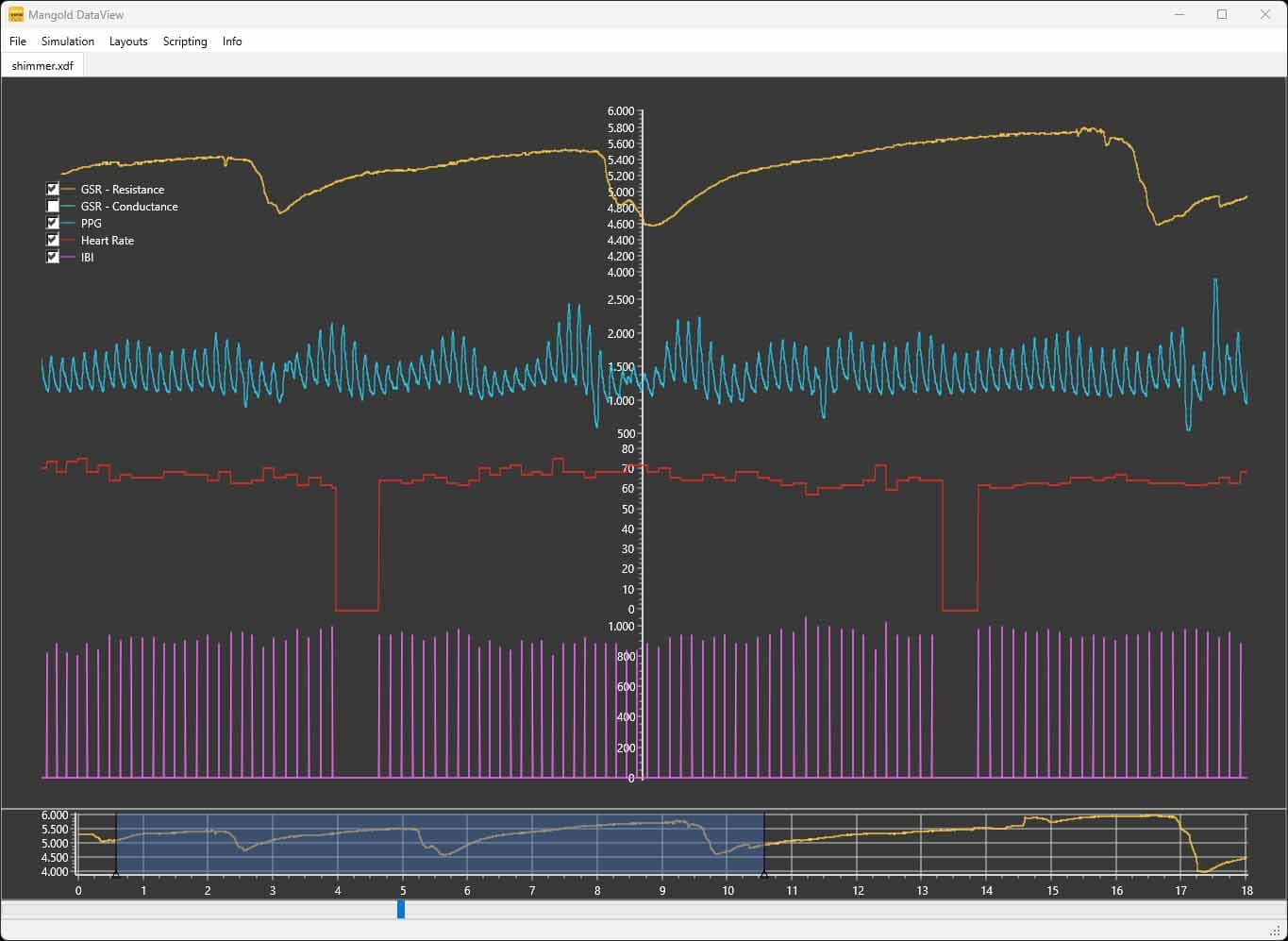
GSR - Galvanic Skin Response
Galvanic Skin Response (GSR), also known as Electrodermal Activity (EDA) or Skin Conductance Response (SCR), is a physiological phenomenon that reflects changes in the electrical conductance of the skin in response to various stimuli, both internal and external.
It is often used as an indicator of emotional and psychological arousal.
The human skin is equipped with sweat glands that are controlled by the autonomic nervous system, which consists of two branches: the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system.
The sympathetic nervous system is particularly involved in the body's "fight or flight" response, which is activated during situations of stress, excitement, or anxiety. When the sympathetic nervous system is activated, it causes the sweat glands to release sweat, leading to changes in the skin's electrical conductance.
Galvanic skin response is measured using electrodes that are typically placed on the surface of the skin, usually on the fingers or palms.
These electrodes pass a small electrical current through the skin and measure the resulting changes in skin conductance.
Understanding Galvanic Skin Response involves several key factors:
In summary, Galvanic Skin Response is a physiological phenomenon that reflects changes in skin conductance due to the activity of sweat glands, influenced by the sympathetic nervous system's response to various stimuli. It is a valuable tool in psychology and physiology research for assessing emotional and psychological arousal.
HRV - Heart Rate Variability
Heart Rate Variability (HRV) refers to the variation in the time interval between successive heartbeats, also known as R-R intervals, which are measured from the peak of one heartbeat to the peak of the next.
HRV is an important physiological parameter that reflects the dynamic balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) and provides insights into the adaptability and regulation of the cardiovascular system.
The autonomic nervous system consists of two main branches:
Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS): This branch is responsible for the "fight or flight" response and is associated with physiological arousal, stress, and the mobilization of energy resources. It increases heart rate and prepares the body for action.
Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS): This branch is responsible for the "rest and digest" response and promotes relaxation, recovery, and energy conservation. It decreases heart rate and supports activities like digestion and recovery.
Understanding Heart Rate Variability involves several key factors:
In summary, Heart Rate Variability reflects the dynamic interplay between the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches of the autonomic nervous system. By analyzing the variability in time intervals between successive heartbeats, HRV provides valuable insights into cardiovascular health, autonomic regulation, and physiological responses to stress and relaxation.
PPG - Photoplethysmography
Photoplethysmography, commonly referred to as PPG, is a non-invasive optical technique used to measure changes in blood volume within tissue, particularly in peripheral blood vessels.
PPG is often utilized to monitor various physiological parameters, including heart rate, pulse rate, and blood oxygen saturation (SpO2). It involves the use of light to assess the pulsatile nature of blood flow in the microvascular bed beneath the skin.
Here's a scientific explanation of PPG:
In summary, Photoplethysmography is an optical technique that utilizes the interaction between light and blood volume changes in tissue to measure physiological parameters like heart rate, pulse rate, and blood oxygen saturation. By analyzing variations in light absorption or transmission, PPG provides valuable information about blood flow and oxygenation in peripheral blood vessels.
IBI - Interbeat Interval
IBI stands for Inter-Beat-Interval, and it refers to the time duration between successive heartbeats, also known as R-R intervals. The measurement of IBI is crucial in understanding heart rate variability (HRV) and assessing the rhythmic patterns of heartbeats.
IBI data is commonly used in medical and physiological research to gain insights into the autonomic nervous system's activity, cardiovascular health, and various physiological conditions.
Here's a scientific explanation of IBI:
In summary, Inter-Beat-Interval (IBI) refers to the time duration between consecutive heartbeats, also known as R-R intervals. It plays a crucial role in assessing heart rate variability (HRV) and autonomic nervous system function. By analyzing IBI data, researchers and clinicians gain insights into cardiovascular health, stress levels, and autonomic control of the heart's rate and rhythm.
Interested in Measuring Physiology? Contact us today
We are happy to show you how Mangold DataView can be used in your project.
Just get in touch with us...
Or send an email to
