Neuromarketing
Neuromarketing represents a cutting-edge intersection of neuroscience and marketing, aimed at unraveling the mysteries of consumer decision-making. This article delves into the realm of neuromarketing, exploring its foundational principles, methodologies, ethical considerations, and the transformative impact it holds for the marketing landscape.
Decoding Consumer Behavior with Brain Science
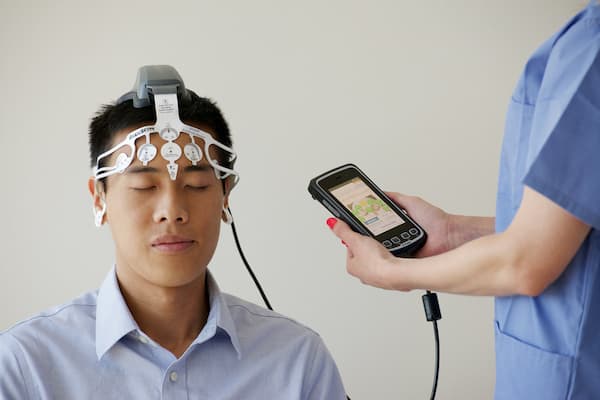
Neuromarketing is a discipline that utilizes neuroscientific tools and techniques to uncover the cognitive and emotional processes underlying consumer behavior.
Here´s an extensive examination of the key tenets of neuromarketing and its significance in understanding the intricacies of consumer decision-making.
Core Principles of Neuromarketing
- Emotional Engagement: Investigating the emotional responses triggered by marketing stimuli, acknowledging the powerful role emotions play in consumer choices.
- Implicit Memory: Exploring how subconscious memories influence brand perception and decision-making, even when consumers are unaware of these influences.
- Attention and Perception: Studying how consumers allocate attention and perceive stimuli to optimize marketing materials for maximum impact.
- Neuroeconomics: Integrating economic theories with neuroscience to understand the neural mechanisms behind purchasing decisions and pricing strategies.
Methodologies in Neuromarketing
- Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI): Mapping brain activity to identify neural responses associated with specific marketing stimuli.
- Electroencephalography (EEG): Recording electrical activity in the brain to measure attention, engagement, and emotional responses in real-time.
- Eye-Tracking: Monitoring eye movements to assess visual attention and identify focal points in advertising materials.
- Biometric Measurements: Utilizing physiological indicators like heart rate, skin conductance, and facial expressions to gauge emotional responses.
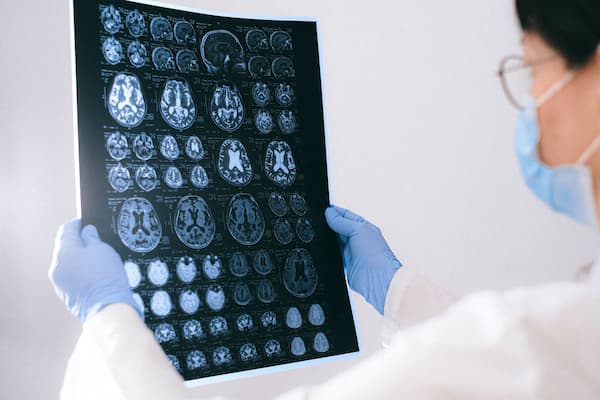
Ethical Considerations in Neuromarketing
- Consumer Privacy: Addressing concerns related to the collection and utilization of sensitive neuroscientific data, ensuring ethical practices in research.
- Transparency: Communicating the use of neuromarketing techniques to consumers, fostering trust and transparency in marketing practices.
- Consent and Voluntariness: Ensuring participants provide informed and voluntary consent before participating in neuromarketing studies.
Transformative Impact on Marketing
Neuromarketing has revolutionized traditional marketing strategies by providing unprecedented insights into consumer preferences, enabling marketers to create more targeted and impactful campaigns.

Marketing team meeting
Limitations and Challenges
- Interpretation Complexity: Navigating the intricate process of interpreting neuroscientific data and translating it into actionable marketing insights.
- Sample Size and Generalizability: Addressing challenges associated with small sample sizes in neuroscientific studies and ensuring findings can be generalized to broader populations.
Future Directions
- Personalized Marketing: Leveraging neuromarketing insights for personalized advertising tailored to individual preferences.
- Neurotechnology Advances: Exploring emerging technologies that enhance the precision and accessibility of neuroscientific measurements.

New York City´s Time Square, the worlds most iconic advertising site
Conclusion
Neuromarketing represents a paradigm shift in understanding consumer behavior by delving into the intricacies of the human brain. As technology advances and ethical standards evolve, the fusion of neuroscience and marketing will continue to shape the future of advertising, offering a deeper understanding of consumers and paving the way for more effective and ethical marketing strategies.
